Agile scrum methodology is a sprint-based project management system with the goal of delivering the highest value to stakeholders.
- With a few major distinctions, agile and scrum are two similarly structured project management methodologies.
- While scrum is more strict and encourages cross-functional teams, agile is more flexible and supports leadership teams.
- Agile enables more effective collaborations between teams working on difficult projects by allowing teams to create projects in manageable chunks known as “sprints.”
- This article is intended for project managers and company owners who are interested in learning more about the agile scrum methodology and how to apply it to management processes.
Companies of all sizes adopt the agile scrum approach because it enables excellent project-based teamwork and productivity. The agile scrum technique is the most widely used use of agile. Agile and scrum are two distinct methodologies that may be utilized individually. The whole guide on agile scrum methodology is available here.
How does agile scrum work?
The agile scrum technique combines the scrum framework and the agile mindset.
Agile refers to incremental development, enabling teams to create projects in manageable chunks.
One of the numerous varieties of agile technique is scrum, which is recognized for segmenting projects into sizeable units called “sprints.” Agile scrum technique is advantageous for companies that must complete certain projects fast.
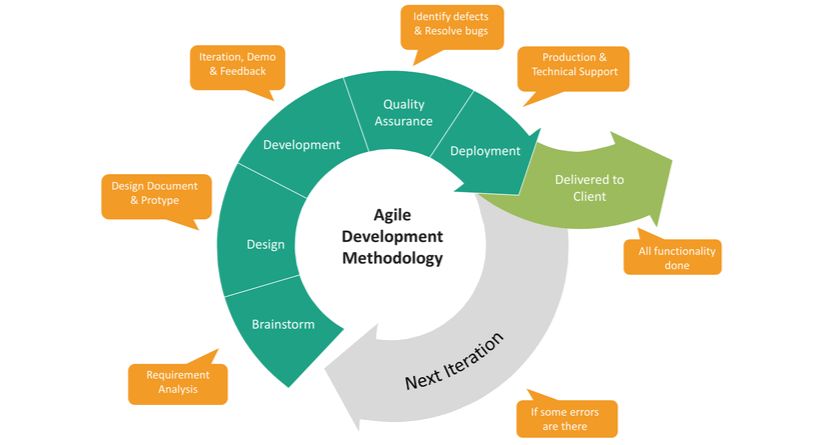
Agile scrum methodology is an incremental development-based approach to project management.
Each iteration consists of two to four-week sprints, with the aim of completing the most crucial features first and producing a potentially marketable product at the end of each sprint.
In succeeding sprints, the product is expanded, and adjustments are made in response to stakeholder and consumer input in between sprints.
Agile scrum methodology is centered on delivering multiple iterations of a product to stakeholders in order to deliver the highest business value in the shortest amount of time, in contrast to other project management methods that emphasize building an entire product in a single operation from beginning to end.
The agile scrum technique has several advantages.
First, since each set of goals must be accomplished inside each sprint’s time limit, it promotes the development of products more quickly.
It also necessitates regular goal-setting and planning, which aids the scrum team in concentrating on the goals of the current sprint and boosting output.
What is agile?
By segmenting a project into manageable stages that each allow for regular discussion with stakeholders to foster improvements at every level, the agile method enables a team to manage a project more effectively.
What principles underpin agile?
In order to find a new way to write software, a group of developers created the Agile Manifesto in 2000, which is where Agile was first introduced. Four values are listed in the manifesto:
- Persons and relationships, rather than procedures and tools
- Functional software above thorough documentation
- Customer involvement during contract negotiations
- Adapting to change vs sticking to a plan
What are the 12 agile tenets?
Additionally, the Agile Manifesto included 12 software development-related principles, which were eventually modified to take a broader view of users:
- consumer contentment
- Continuous and early delivery
- Accept change
- Regular deliveries
- collaboration between developers and companies
- persons with motivation
- a face-to-face discussion
- Functioning goods
- technical mastery
- Simplicity
- Self-contained groups
- Regulation, contemplation, and modification
How do you scrum?
Scrum is a framework for successful team interactions when working on complicated goods, to put it briefly. Scrum is a kind of agile technology that uses meetings, roles, and tools to improve teamwork and task management for teams working on complicated projects.
Scrum may be helpful to any team working toward a similar objective, even if software development teams are the ones that utilize it the most frequently.
Who will gain from a scrum?
Although scrum may be helpful for many different types of firms and projects, the following are the most probable winners:
- Complicated Projects: that need teams to finish a backlog are best suited for the Scrum approach. Scrum simplifies big projects by breaking down each step into manageable pieces.
- Companies that value outcomes: Scrum is advantageous for organizations that prioritize results above the tracking of process progress. This is so that results may be driven by efficiency and creativity rather than a thorough, strict procedure, which is what scrum focuses on.
- Companies that provide customer service: Scrum may aid businesses that create goods based on the tastes and requirements of their consumers. Scrum’s ability to react to change makes it essential for meeting client demands.
What are the benefits of agile scrum methodology?
The following are a some of the overall advantages of the agile scrum methodology:
- adaptability and pliability
- Innovation and creativity
- lower prices
- Quality augmentation
- Organizational coordination
- employee happiness
- consumer contentment
The flexibility of the agile scrum technique is its main advantage. The scrum team often receives feedback from stakeholders following each sprint when using the sprint-based approach.
The scrum team may easily and swiftly modify product goals throughout next sprints to deliver more beneficial iterations if there are any issues or adjustments.
Stakeholders are pleased as a result of getting precisely what they wanted after being involved at every stage.
Contrast this with conventional project management methods, where stakeholders seldom offer input and time is wasted making adjustments to the product in the middle of the development process, or even worse, when teams are forced to start over after the product has already been developed.
An internal scrum specialist or an external consultant is required to guarantee that scrum principles are being utilized effectively while implementing agile scrum methodology.
Agile scrum approach requires exact execution and, if not done correctly, might lead to major issues.
What are the different roles in agile scrum methodology?
There are two kinds of jobs in the agile scrum methodology: the core roles, also known as “pigs,” and the supplementary roles, often known as “chickens.”
- Scrum master: product owner, and scrum team are the three main roles. These individuals are all devoted to the scrum project.
- The facilitator of the scrum development process is known as a scrum master. The scrum master not only holds daily meetings with the scrum team but also ensures that the scrum rules are being followed and used as intended. Along with mentoring and inspiring the team, the scrum master is also responsible for removing obstacles from sprints and making sure the team is in the best environment possible to accomplish its objectives and generate deliverables.
- Owner of the product: Customers are often considered stakeholders by the product owner. The product owner establishes product expectations, tracks product changes, and manages a scrum backlog, a comprehensive and continuously updated to-do list for the scrum project, to make sure the scrum team is consistently providing value to stakeholders and the company. The product owner is also in charge of ranking each sprint’s goals according to their importance to the stakeholders so that the most crucial and deliverable features are created in each iteration.
- Scrum team: A self-organized team of three to nine people who has the business, design, analytical, and development abilities necessary to carry out the real job, solve problems, and generate deliverable products is known as a scrum team. The scrum team’s members self-manage tasks and share accountability for achieving each sprint’s objectives.
On the other side, ancillary responsibilities are played by other stakeholders who are active but not committed to the scrum project. Customers, managers, and members of the executive team typically play supplementary roles in businesses.
They are involved for consulting, reporting progress, and receiving feedback in order to give the maximum value possible.
What is the training for scrum and agile?
Scrum and agile training is available to managers and staff through a variety of online and live courses. Scrum or agile techniques certification is available through a variety of educational training programs.
Agile training equips the learner with the fundamentals of the methodology and teaches them how to apply it to the rest of their team.
Similar training is offered by scrum, including an introduction to agile practices; however, the training is exclusive to the scrum framework.
You must first study and grasp the fundamentals of scrum through videos or a quick online search in order to become a certified scrum master (CSM) or certified scrum product owner (CSPO).
Next, look online or at your place of employment for an appropriate CSM or CSPO course. To get certified after completing the course, you often need to pass an exam.
Following certification, you are qualified to guide your team through the scrum process or offer information on the scrum product.
What are the differences between scrum and agile?
Despite their similarities, scrum and agile differ in the following significant ways:
- Agile appreciates flexibility more than Scrum values rigidity.
- Agile leaders are essential, because scrum encourages a cross-functional team that can work independently.
- Agile and scrum both entail face-to-face meetings between members of cross-functional teams, however agile also uses stand-up meetings every day.
- While scrum may be inventive and adventurous, agile is designed to be kept as basic as possible.
- Agile delivers everything at the conclusion of the process, whereas Scrum delivers smaller, independent tasks.